This is the last part of our discussion on gardening in soils that contain heavy metals (you can catch up on part 1 and part 2 if you need to). Today we’ll focus on the strategies you can use in your gardens and landscapes to reduce your exposure to soil-borne heavy metals.

Test your soil!
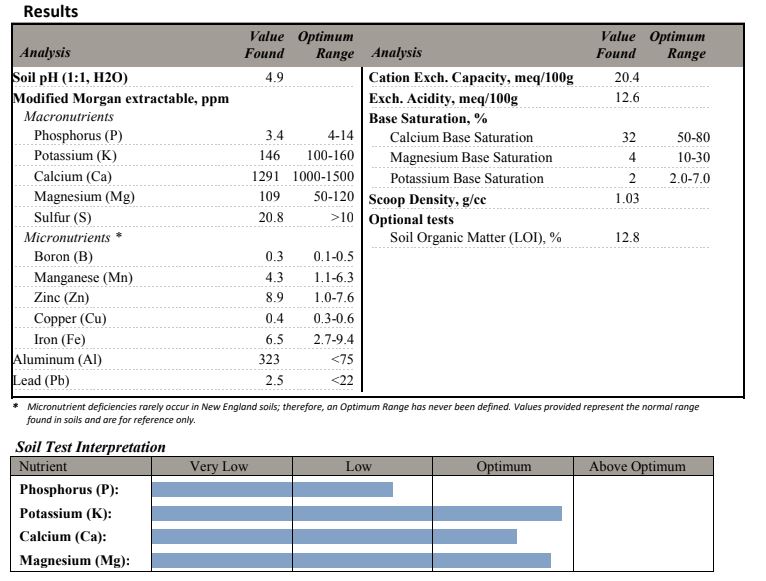
First – and this should really go without saying – you must test your soil to determine if it contains heavy metals of concern. The COVID19 pandemic provides the perfect comparison: you can’t assume you don’t have the virus just because you don’t have symptoms, and you can’t assume your soil doesn’t have toxic heavy metals just because you don’t think it does. The only way to know for sure, in either case, is through testing.

Most soil tests routinely report aluminum, lead, zinc, and aluminum. Other metals, such as arsenic, cadmium, and chromium, may not be part of a basic soil test and you will need to request additional tests if these metals are likely to be present. Often, county health offices will provide free soil testing if you live in a region where there are known contaminants. For example, I live in the Tacoma area where large amounts of arsenic were deposited for decades downwind of an aluminum smelter. Residents of Pierce County can get free soil testing because of the potential danger.
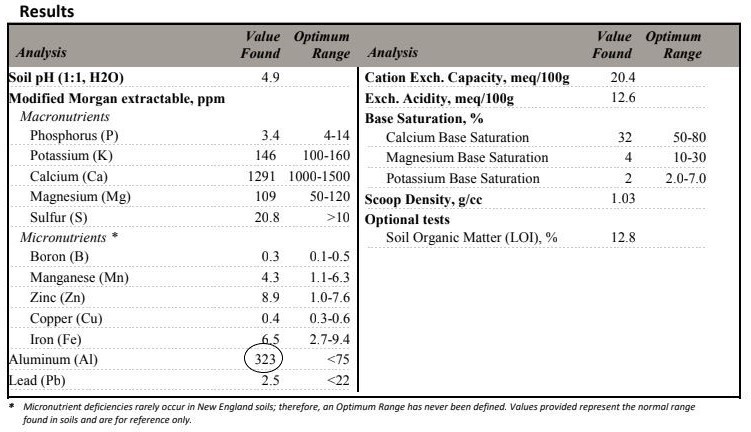
Even if you don’t live in an area where industrial or agricultural activity may have added toxic heavy metals to your soils, your soil may naturally contain high levels of some metal of concern. As I’ve mentioned in a previous post, our soils have high levels of aluminum. Because we are not downwind of the smelter site mentioned above, I would not have assumed we had any metals of concern, given the rural location of our land, but knowing this informs my choice of vegetables to plant.

Avoid adding more heavy metals
Fortunately, many of the consumer products that contained heavy metals are now gone and no longer will add to existing levels of soil metals. But there are still sources out there that gardeners are well-advised to avoid.
- Older treated timbers. As mentioned in my first post, landscape timbers were once treated with a chemical preservative containing arsenic and chromium. Even though gardeners love reusing materials (we are a thrifty bunch!), these older timbers should be removed if they are still on your property. New timbers are treated with a copper-based solution, which is a more environmentally friendly preservative.
- Kelp-based fertilizers and amendments. While these products are wildly popular with gardeners, they aren’t very effective fertilizers. Moreover, some kelp species accumulate heavy metals, like arsenic, in seawater and these metals will become a permanent part of your soils. Take a look at this fact sheet for more information.
- Recycled rubber mulch. This product should be avoided for many reasons (you can read more about the problems in this fact sheet). As it disintegrates it releases high levels of zinc into the soil. And while zinc is an essential micronutrient in plants (and people!), high levels are toxic.
- Unregulated composts and organic products. Certified composts and other organic products have been tested for pesticide residues and heavy metals: unregulated products have not. Unless you are making your own compost from materials you know to be free from contamination, your safest bet is to purchase certified products.

Rubber mulch 
Kelp meal 
Older treated timbers 
If you don’t know what’s in it – don’t use it.
If you have materials like old timbers, you should never burn them or throw them away. They need to be disposed of as a hazardous waste, much like old cans of paint, mercury-containing thermometers, etc. Eventually, we may be able to use these hazardous discards for biofuel production through pyrolysis, or extract the heavy metals from them for reuse. For now, just dispose of them in a legal and environmentally responsible way.

Suggestions for safe gardening
If soil testing reveals high levels of metals of concern, there are work-arounds to allow you to still enjoy growing vegetables safely. If your soil tests reveal that your soil is safe for growing edibles, congratulations! You may still benefit from some of the suggestions below.
- Cover exposed soil with ground covers and mulches (coarse organic or inorganic materials) to eliminate metal-laden dust.
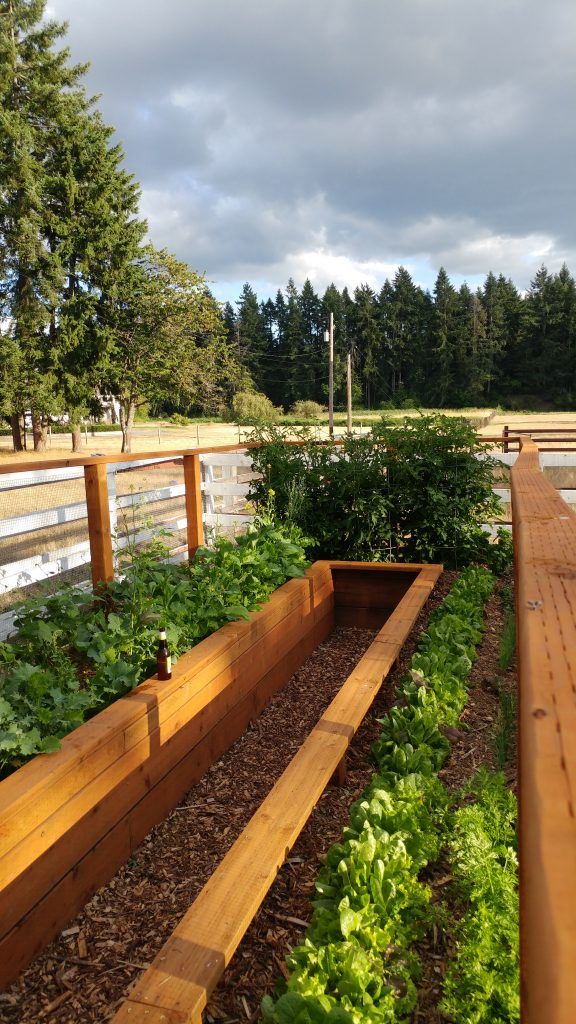
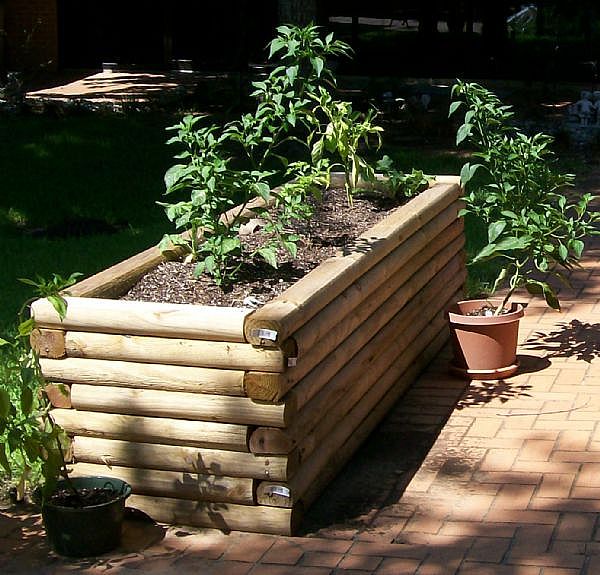
- Create raised beds for edibles using untreated wood or other metal-free materials. Line the bottom of the bed with an impermeable membrane to prevent movement of soil-borne metals into the beds.
- If raised beds are not possible, use large containers to grow edibles.
- Avoid using galvanized tubs, as they will leach zinc (and sometimes chromium) into the soil.
- Fill beds and containers with clean (i.e., tested) soils or potting media.
- Don’t plant vegetables near roadways, which are a source of airborne lead.

Have I mentioned how great arborist wood chips can be in gardens? 
Container gardening is easy and mobile 
It looks cute…but just don’t use galvanized tubs for edibles 
While this may seem like a good use of space, the location next to a roadway means lead expsoure will be a chronic problem