This article was originally published (surprisingly?) by the Mother Earth News Blog.
What do the words on your food (or garden supplies) labels mean? Do you know the difference between organic, natural, and sustainable? Are there rules about who can use which labels? When you are shopping at the farmers market or grocery store, or when you’re buying seeds or plants at the garden center, it is important to know what the words used to describe the product mean. It is also important to understand that some words have different meanings to different people and sometimes are used more for marketing (and sometimes misleading customers) than conveying actual meaning. Let’s take a look at some of the words that have an “official” definition, some where the meaning can be interpreted differently, and some that can be misleading or misinterpreted.
“Official” words for foods and plants
There are a handful of words that you’ll find at the grocery store, farmers market, or garden center that have an official definition because they are either part of a law or code or are part of an official certification process.

For example, in the US for a product to bear the term “certified organic” or “organic“, it must be produced in accordance with the National Organic Program organic certification process outlined in federal policy/law and administered by the USDA. While there are many minute details for organic production, the “big picture” definition is that only organic/naturally occurring soil amendments and pesticides can be used – typically from a biological or elemental source. It is important to note that organic does not mean pesticide free. Repeat: ORGANIC DOES NOT MEAN PESTICIDE FREE
The organic certification process can be costly and time consuming, and some producers feel that restrictions do not go far enough, so alternative certifications have been developed such as Certified Naturally Grown and Regenerative Organic Certified. These certifications are not administered by the USDA, but rather by individual organizations that have developed them.
Another term that has emerged is “biodynamic,” which marries some organic principles with the requirement that the farm be a “closed system”, meaning that outside inputs like fertility are not used. Biodynamic production also requires the use of “preparations” that would be described as mystical or homeopathic and must be practices in accordance with “energies” such as the phase of the moon. In order to be labeled “biodynamic” a product must be certified by Demeter USA. Our very own LCS has addresses the “pseudoscience” of biodynamic growing in a previous paper. As a science-based group, we consider biodynamic to mainly be WOO.
A number of other certifications exist, such as Certified Animal Welfare Approved and Salmon Safe that guarantee things like best practices in livestock welfare and proper wild fishing practices.
“Unofficial” words for growing and marketing
While “official” words have certifications that standardize their meaning across industries, other words we use for production and marketing don’t have official meanings and are often up for interpretation. In instances where a relationship exists between a consumer and producer, say a customer buying directly from a farmer at the farmers market, a conversation can take place to share the meaning of what the words mean. In situations like a product at the grocery store, words are often left to the interpretation of the customer.
For example, while the term “organic” or “certified organic” requires official certification, using the term “organically grown” does not. Many small farmers will use this term to reflect their use of organic practices, but their understanding of practices may deviate from the “official” definition. The term natural or naturally grown may also be used to describe produce or products at the grocery store but no officially sanctioned definition exists. When customers and growers/producers can discuss what the terms mean, an understanding can be developed. However, when such a relationship doesn’t exist, it is hard to know what the terms mean. For example, an ad might say that a product is “natural, so you know that it’s good” to which I might joke that poison ivy and rattlesnake venom are both natural, but that doesn’t mean it is good for you.
The term “local” also doesn’t have a specific definition and can vary widely depending on the context. At farmers markets, it is up to the organization operating the farmers market to create vendor rules and decide what makes sense for each individual market, according to the national Farmers Market Coalition. For example, the closest meat producer may be farther outside of the city than the closest produce farmer. Markets in urban areas may need to recruit vendors from a bit farther away than those in the suburbs. If you have questions about the rules of your local market or where a vendor is farming – just ask! At a grocery store, local can mean whatever the chain wants to decide. Sometimes this can mean in the same state or other times it is regional. Often food at the grocery store will have a label saying the town or region it came from for you to learn more about each specific item.

The terms sustainable and regenerative might be used to describe production practices or a farmer’s philosophy on production. While there aren’t official definitions, the USDA Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education program defines sustainable agriculture as holistic farming practices that balances environmental stewardship, profitability, and personal/social benefit. Though most use of the term sustainable for marketing focuses on the environmental aspect. Regenerative agriculture is a relatively new philosophy of production practices that focus on environmental stewardship to reverse climate change and/or environmental degradation and social fairness and often involves improving soil health. While the terms sustainable and regenerative might seem interchangeable, there are differences (mainly around economic sustainability and around maintaining current environmental conditions vs. improving them). We’ll see how the “regenerative” term plays out – as many consider it to be a “buzzword” in some ag circles.
Words that can confuse or mislead
While there are words that may seem abundantly clear to the person using them, the information or intent may seem totally different to the audience. These words are often used as buzzwords for marketing or may be used to create a sense of fear that is misunderstood. For these words, alternative words or further explanation might reduce confusion.
One such word that is often used is chemical-free. This is often used to describe produce or food that is produced without pesticides. However, use of chemical-free can be misinterpreted and misunderstood. It may be a facetious response, but as a scientist I often cringe when I hear this word used at the farmers market because that I know that everything is made of chemicals – all rocks, plants, animals, humans, and even air and water – are chemicals. Some say that the use of this term is based in fear of pesticides (even organic ones) or is based in anti-science “chemophobia” rhetoric. Using a more precise term, such as pesticide-free conveys the same message without anti-science connotations and reduces the chance of misinterpretation.
Non-GMO is also another term that was created as a fear-based marketing term that has become pervasive at the grocery store, the seed rack, and the farmers market. While there are concerns AND benefits to genetic engineering technology, use of the term non-GMO is often redundant and confusing to consumers because, as it turns out, there are very few opportunities for gardeners, farmers, or consumers to interact with bioengineered crops. Most bioengineered crops are those that are produced as commodities – field corn, soybeans, sugar beets, cotton, canola, etc. Only a handful of crops are those that you’d find at the farmers market or produce section – sweet corn, summer squash, papaya, and one apple cultivar. But these crops are grown in very small amounts, are not available to small-scale farmers or home gardeners, are sold only in larger quantities, and require a contract for purchase. Most produce items grown in the US do not currently have a genetically engineered counterpart – there are no GMO lettuces, radishes, etc. So labeling a tomato as non-GMO is redundant and has unfortunately caused so much confusion and fear amongst consumers that many specifically demand or seek non-GMO tomatoes, even though all tomatoes are non-GMO. There is a third-party certification process through the Non-GMO Project (they’re the ones you see with the butterfly logo on almost every product, even bottled water and salt), however given the confusion and misinformation around the term, the US government recently created a standard “Bioengineered” labeling requirement for all produce and products that consist of or contain genetically engineered crops or ingredients.
A few more words on words…
While words can inform and confuse, being an educated consumer (or producer) can help reduce confusion and help us understand the food that we eat. While we haven’t covered every word you might encounter on a label here, researching words you see can help build your label vocabulary. Building interest in learning about where your food comes from should be a fun way to connect with what is on your plate and who is in your community. Go out there and enjoy the learning process! You can check out some more words related to agriculture and food here.
This article by John Porter was written as part of a partnership in collaboration with staff at the Farmers Market Coalition (FMC) as part of FMC’s partnership with Mother Earth News Fair.
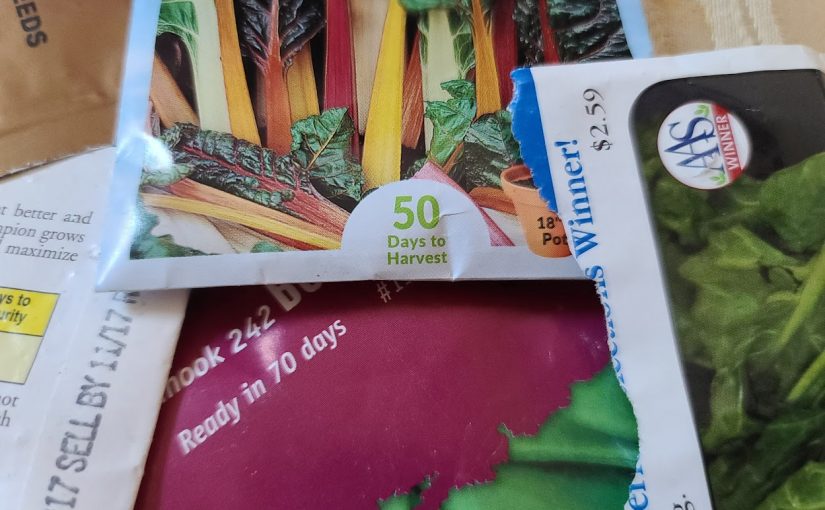
More about seed packet lingo here.